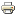
The French Defense is a chess opening characterized by the moves: 1. e4 e6. It is a solid and flexible opening that can be used by both Black and White, although it is more often played by Black.
One of the main ideas behind the French Defense is to occupy the center of the board with pawns, while simultaneously controlling the d5 square. This can be achieved by playing ...d5, which blocks the pawn on e4 and threatens to capture it. The French Defense is a popular choice for Black because it allows them to fight for the center of the board from a solid and flexible position.
Do you want to see all the French defense variations and openings even played. Just download our biggest over the board chess database in the world with 9.2 million human chess games.
Tarrasch Defense
The main variations of the French Defense is the Tarrasch Defense, which is characterized by the moves: 1. e4 e6 2. d4 d5 3. Nd2. This variation is named after the famous chess player Siegbert Tarrasch, who was known for his aggressive and tactical play. In the Tarrasch Defense, White aims to occupy the center of the board and build a solid pawn structure, while Black seeks to undermine White's center with the move ...d5.
Advance and Winawer Variations
Another popular variation of the French Defense is the Advance Variation, which is characterized by the moves: 1. e4 e6 2. d4 d5 3. e5. In this variation, White seeks to occupy the center of the board and build a solid pawn structure, while Black looks to undermine White's center with ...c5. The Advance Variation is a popular choice for White because it allows them to control the center of the board and build a strong pawn structure.
The Winawer Variation is another important variation of the French Defense, and is characterized by the moves: 1. e4 e6 2. d4 d5 3. Nc3 Bb4. In this variation, Black seeks to exchange their dark-squared bishop for White's knight, and then use the resulting pawn structure to launch a counterattack against White's center. The Winawer Variation is a popular choice for Black because it allows them to fight for the center of the board and build a solid pawn structure.

The French Defense is a solid and flexible opening that can be used by both Black and White. It is characterized by the moves 1. e4 e6, and aims to occupy the center of the board and control the d5 square. There are many variations of the French Defense, including the Tarrasch Defense, the Advance Variation, and the Winawer Variation. Each of these variations has its own unique characteristics and strategies, and they can be used by players of all skill levels.
Play all the possible variations of the French defense and remember Practise makes perfect.
The Encyclopaedia of Chess Openings includes an alphanumeric classification system for openings that is widely used in chess literature. Codes C00 to C19 are the French Defence, broken up in the following way (all apart from C00 start with the moves 1.e4 e6 2.d4 d5):
- C00 – 1.e4 e6 without 2.d4, or 2.d4 without 2...d5 (early deviations)
- C01 – 2.d4 d5 (includes the Exchange Variation, 3.exd5)
- C02 – 3.e5 (Advance Variation)
- C03 – 3.Nd2 (includes 3...Be7; C03–C09 cover the Tarrasch Variation)
- C04 – 3.Nd2 Nc6 (Guimard Variation)
- C05 – 3.Nd2 Nf6
- C06 – 3.Nd2 Nf6 4.e5 Nfd7 5.Bd3
- C07 – 3.Nd2 c5 (includes 4.exd5 Qxd5)
- C08 – 3.Nd2 c5 4.exd5 exd5
- C09 – 3.Nd2 c5 4.exd5 exd5 5.Ngf3 Nc6
- C10 – 3.Nc3 (includes the Rubinstein Variation, 3...dxe4)
- C11 – 3.Nc3 Nf6 (includes the Steinitz Variation, 4.e5; C11–C14 cover the Classical Variation)
- C12 – 3.Nc3 Nf6 4.Bg5 (includes the McCutcheon Variation, 4...Bb4)
- C13 – 3.Nc3 Nf6 4.Bg5 dxe4 (Burn Variation)
- C14 – 3.Nc3 Nf6 4.Bg5 Be7
- C15 – 3.Nc3 Bb4 (C15–C19 cover the Winawer Variation)
- C16 – 3.Nc3 Bb4 4.e5
- C17 – 3.Nc3 Bb4 4.e5 c5
- C18 – 3.Nc3 Bb4 4.e5 c5 5.a3 (includes the Armenian Variation, 5...Ba5)
- C19 – 3.Nc3 Bb4 4 e5 c5 5.a3 Bxc3+ 6.bxc3 Ne7 7.Nf3 and 7.a4
Visit and subscribe to our YouTube channel  to learn chess openings and much more.
to learn chess openings and much more.